The Ultimate Guide to Competitive Intelligence: Tools, Strategies, and Insights

What is Competitive Intelligence?
When I first started tracking competitors, I made the classic mistake. I collected too much data but had no idea how to use it. I had reports on their pricing, ad spend, product launches, and customer reviews, yet I had no real insights. I was drowning in information without a clear strategy.
That’s when I realized competitive intelligence is not just about tracking competitors. The real advantage comes from analyzing patterns, spotting opportunities, and making strategic moves before competitors do. Instead of collecting data for the sake of it, the focus should be on turning information into decisions that drive growth.
Key Focus Areas
✔ Competitor tracking. Monitor pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, product launches, and customer engagement.
✔ Market trend analysis. Identify shifts in consumer demand and industry movements before they go mainstream.
✔ Strategic decision-making. Use competitor insights to refine business strategies, capitalize on weaknesses, and uncover new growth opportunities.
Competitive intelligence is not about watching the competition. It is about staying ahead of them.
Why Is Competitive Intelligence Important in Today’s Business Environment?
I used to think that if I just focused on my own business, I would be fine. But I learned the hard way that ignoring competitors is a risk you cannot afford to take. One day, a competitor launched a product nearly identical to mine, but with better pricing and a stronger marketing push. By the time I noticed, they had already captured a huge chunk of the market.
That was my wake-up call.
Competitive intelligence is not about obsessing over competitors. It is about protecting and growing your business.
Benefits of Competitive Intelligence
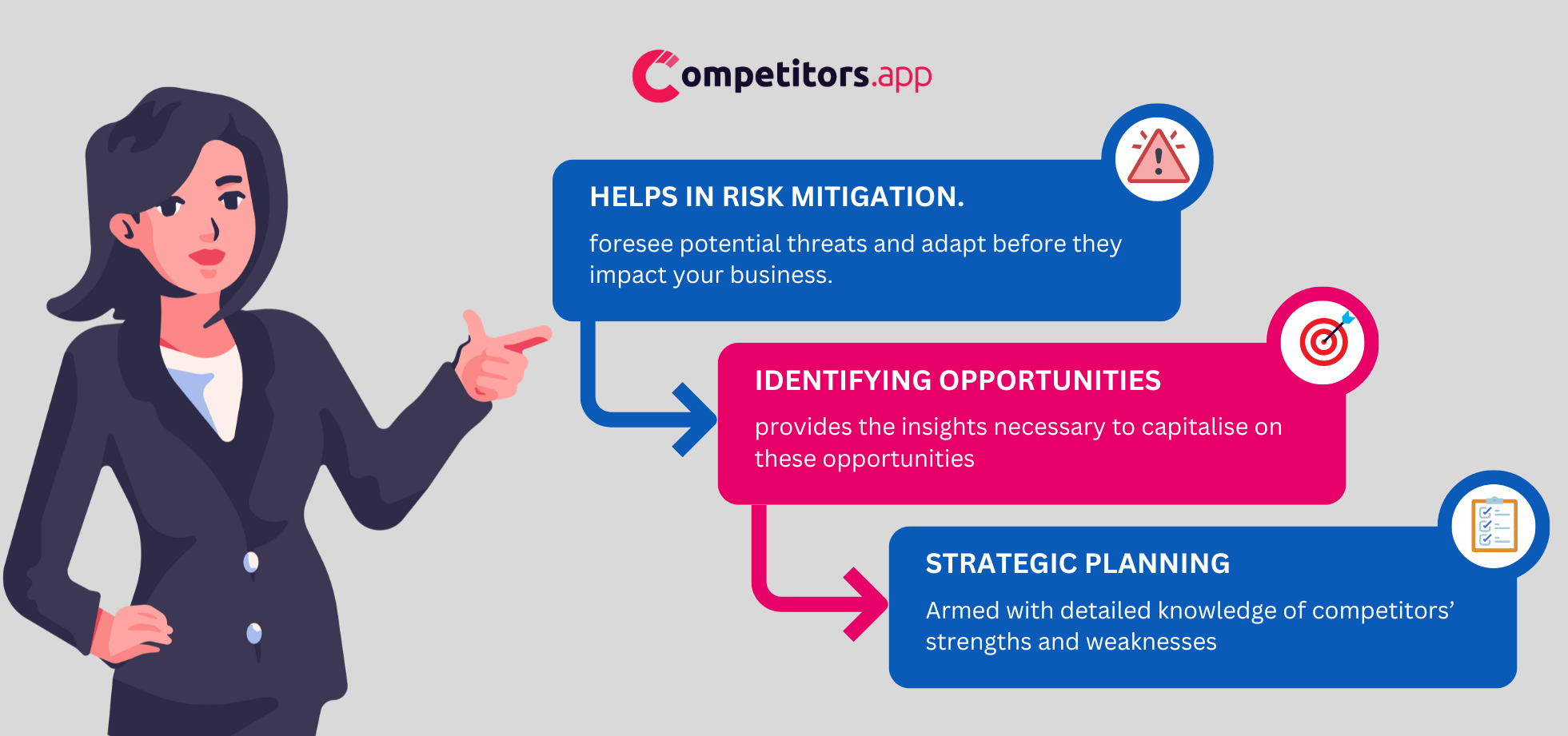
Risk Mitigation. Market shifts can happen fast. Competitive intelligence helps you spot threats before they impact your business. Whether it is a pricing war, a new product launch, or an industry change, staying informed allows you to act early instead of scrambling to catch up.
Identifying Market Gaps and Opportunities. Every missed opportunity is one your competitors could take. By analyzing their strategies, you can uncover untapped customer needs and move fast before they do. If a competitor is failing to address a common frustration, that is your chance to step in and provide a better solution.
Sharpening Your Strategy. It is not just about knowing what competitors are doing. It is about using that knowledge to position your business more effectively. By studying their strengths and weaknesses, you can refine your messaging, optimize your product, and make smarter moves that give you an edge.
Competitive intelligence is not about reacting but rather about staying ahead.
The Evolution of the Competitive Intelligence Industry
I still remember when tracking competitors meant digging through trade magazines, scanning industry reports, and attending conferences just to get a small piece of the picture. Everything was slow, outdated, and imprecise by the time decisions were made. Competitive intelligence was more of a guessing game than a strategy.
Today, it is an entirely different story. What once took weeks now happens in real time, with AI and automation doing the heavy lifting.
The Evolution of Competitive Intelligence
Early Methods. Competitive intelligence started as a manual, time-consuming process. Businesses relied on public records, trade publications, and industry events to gather insights. Finding valuable information meant sifting through archives, conducting in-person interviews, and waiting for industry reports to be published. The process was slow and often outdated by the time decisions were made.
The Digital Shift. The internet changed everything. Suddenly, businesses had access to competitor websites, financial reports, and news updates. Information became easier to collect, but managing the flood of data became a challenge. I remember the first time I tried gathering competitor insights online. It felt like drinking from a firehose. Without the right tools, separating valuable insights from noise was nearly impossible.
The Rise of AI and Automation. Today, competitive intelligence is powered by AI-driven tools that automate data collection, analysis, and reporting. Platforms like SEMrush, Competitors App, and SimilarWeb track competitor activity in real time, offering insights that used to take weeks to uncover. Businesses no longer need to guess where the market is heading. They can now predict trends and adjust before competitors do.
Industry-Wide Adoption. Competitive intelligence is no longer reserved for large corporations. Tech companies, healthcare providers, retailers, and even startups now rely on real-time competitive insights to stay ahead. I have seen businesses completely pivot their marketing strategies overnight because they identified an emerging trend through competitive tracking.
Competitive intelligence has gone from a tedious manual process to an AI-powered advantage. The companies that embrace it are not just tracking competitors. They are predicting the future and shaping their industries.
The Goals and Benefits of Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence is not just about tracking competitors. It is about making smarter decisions that give your business an edge. The best companies do not just react to competitors. They use intelligence to spot opportunities, refine strategies, and stay ahead of market shifts.
What Competitive Intelligence Helps You Achieve
Spot Market Gaps. Find unmet customer needs before competitors do. If they fail to address a common frustration, that is your chance to step in with a better solution.
Improve Products and Services. Understanding how competitors develop their offerings helps refine your own. You do not have to copy. You just have to do it better.
Align with Market Demand. Competitive intelligence tracks pricing trends, customer expectations, and shifting demand to ensure you do not fall behind.
Support Internal Teams. Insights fuel marketing, sales, product development, and executive decisions, helping teams stay aligned and proactive.
How Competitive Intelligence Benefits Your Business
Marketing Teams. Build better campaigns by understanding which competitor strategies succeed and which fail.
Sales Teams. Equip sales reps with real-time competitor insights to counter objections and highlight unique strengths.
Product Teams. Use competitor data to innovate faster and develop features customers actually want.
Leadership and Strategy. Make data-backed decisions instead of relying on assumptions or guesswork.
Competitive intelligence is not about watching competitors. It is about learning from them, improving your strategy, and making decisions with confidence.
How Competitive Intelligence Works
Competitive intelligence isn’t just about collecting data, it’s about analyzing it, applying it, and turning insights into action.
✔ Competitive Intelligence Analysis: Break down competitor strategies, market trends, and customer feedback to identify strengths and weaknesses.
✔ Competitive Marketing Intelligence: Track how competitors position themselves, advertise, and acquire customers.
✔ Competitive Intelligence Research: Pull data from social media, industry reports, financial records, and competitor websites to get a complete picture of the market.
By combining these elements, businesses stay ahead, adapt faster, and outmaneuver the competition, not just react to them.
The Competitive Intelligence Process
Competitive intelligence isn’t just about collecting data, it’s about turning insights into actions that actually move the needle. I’ve seen businesses drown in information without knowing how to use it. The key is having a clear process that helps you focus on what truly matters instead of getting lost in the noise.
Step 1: Identify Your Main Competitors
You need to know exactly who you’re up against prior to doing any analysis. This doesn’t just mean listing every company in your industry, it means identifying the two to three competitors that pose the biggest threat to your growth.
I’ve found that using competitor analysis tools makes this process a lot easier. Instead of guessing, I rely on tools like SEMrush’s Competitors Report to see who ranks for the same keywords and is actively competing for my audience’s attention.
By keeping my focus on the biggest competitive threats, I can track their every move and adjust my strategy before they gain the upper hand.
Step 2: Gather and Organize Data
Competitive intelligence is only as good as the data behind it. If you’re working with incomplete, outdated, or misleading information, you’re making decisions based on guesses rather than facts.
I’ve learned that pulling data from multiple sources is the best way to ensure accuracy. Instead of just checking competitor websites, I use:
✔ SEO tools: Track keyword rankings and content performance
✔ CRM & sales data: See where leads are coming from and what’s converting
✔ Industry reports & publications: Get a bird’s-eye view of market trends
✔ Customer reviews & feedback: Understand what people actually care about
Organizing all this data can be overwhelming, but I always prioritize the most relevant insights rather than collecting everything just for the sake of it.
Step 3: Analyze the Data & Find Actionable Insights
Raw data means nothing unless you know what to do with it. I’ve worked with teams that spent weeks collecting data but had no clear next steps. That’s why analysis is the most critical part of the process.
I use competitor intelligence tools like SEMrush’s Market Explorer to break down SEO trends, while platforms like EyeOn help me track daily, weekly, or monthly competitor activities without having to manually check every site.
Here’s what I look for:
✔ Patterns in competitor behavior: Are they increasing ad spend? Pushing discounts? Doubling down on specific content types?
✔ Emerging trends in the industry: What’s gaining traction that my business can capitalize on?
✔ Competitor weaknesses: Are there gaps in their strategy that I can exploit?
This step is where the real magic happens. Without proper analysis, all the data in the world won’t help you make better decisions.
Step 4: Tailor Your Business Strategy
Competitive intelligence only works if you actually apply what you learn. I’ve seen businesses sit on great insights for months without acting, meanwhile, their competitors move ahead.
After analyzing the data, I focus on practical adjustments to my strategy. This could mean:
✔ Adjusting my pricing strategy to match (or beat) competitors
✔ Refining my marketing messaging based on what’s resonating with my audience
✔ Developing new features or products that fill gaps competitors are missing
✔ Targeting new audiences based on competitor customer feedback
This isn’t about blindly copying competitors, it’s about using competitive intelligence to make my own business stronger and more agile.
Types of Competitive Intelligence

Tactical Competitive Intelligence
- Purpose: Helps businesses react quickly to competitor actions like promotions, pricing changes, or product updates.
- Key Areas:
- Monitoring competitor discounts and pricing adjustments.
- Tracking seasonal trends for inventory and promotions.
- Benefits:
- Ensures quick decision-making.
- Helps businesses stay agile in a competitive market.
Strategic Competitive Intelligence
- Purpose: Guides long-term business strategies by identifying industry trends and potential threats.
- Key Areas:
- Exploring new markets or customer segments.
- Tracking emerging technologies and shifts in consumer behavior.
- Benefits:
- Supports sustainable growth and market positioning.
- Strengthens resilience against industry disruptions.
Market Intelligence
- Purpose: Provides insights into the market landscape, helping businesses identify opportunities and threats.
- Key Areas:
- Monitoring industry trends, demand shifts, and regulations.
- Analyzing market size, growth potential, and competitive saturation.
- Benefits:
- Enhances decision-making for market entry and expansion.
- Improves competitive positioning and adaptability.
Product Intelligence
- Purpose: Helps businesses refine product development by analyzing competitor offerings.
- Key Areas:
- Evaluating product features, pricing, and quality.
- Tracking competitor product launches and customer feedback.
- Benefits:
- Ensures competitive differentiation.
- Helps businesses improve product-market fit.
Sales and Pricing Intelligence
- Purpose: Optimizes revenue generation by tracking competitor pricing and sales strategies.
- Key Areas:
- Monitoring pricing models, discount strategies, and promotional campaigns.
- Analyzing competitor revenue trends and sales performance.
- Benefits:
- Ensures competitive pricing.
- Maximizes profitability and market share.
Marketing Intelligence
- Purpose: Enhances marketing strategies by analyzing competitor tactics and customer engagement.
- Key Areas:
- Tracking SEO rankings, PPC campaigns, and content performance.
- Monitoring competitor advertising strategies and audience interactions.
- Benefits:
- Improves marketing effectiveness and ROI.
- Strengthens audience targeting and brand positioning.
Customer Intelligence
- Purpose: Helps businesses understand competitor customers and identify satisfaction gaps.
- Key Areas:
- Analyzing reviews, social media mentions, and customer feedback.
- Identifying unmet customer needs and recurring complaints.
- Benefits:
- Strengthens customer relationships.
- Helps businesses attract and retain dissatisfied competitor customers.
Operational Intelligence
- Purpose: Evaluates competitor efficiency to identify areas for operational improvement.
- Key Areas:
- Analyzing supply chain, production processes, and logistics.
- Identifying cost-saving strategies competitors use.
- Benefits:
- Improves efficiency and reduces operational costs.
- Enhances profitability and scalability.
Emerging Technology Intelligence
- Purpose: Helps businesses stay ahead by tracking competitor adoption of new technologies.
- Key Areas:
- Monitoring AI, automation, and disruptive tech trends.
- Identifying innovations that impact industry standards.
- Benefits:
- Encourages innovation and adaptation.
- Ensures businesses remain technologically competitive.
Gathering Competitive Intelligence: Sources to look for
Publicly Available Data
Public records reveal key insights into competitors’ financial health, operations, and strategic moves.
- Job postings indicate expansion plans or new capabilities.
- Annual reports highlight revenue streams, market focus, and partnerships.
- Public patents expose innovation pipelines and future product launches.
Social Media and Competitor Hashtags
Social media platforms offer real-time insights into competitor branding and customer interactions.
- Tracking hashtags helps measure competitor campaign success.
- Monitoring reviews and complaints reveals customer pain points.
- Analyzing influencer collaborations uncovers competitor marketing partnerships.
SEO and PPC Tools
SEO and PPC tools decode competitors’ online visibility strategies.
- Identifying top-performing keywords highlights content gaps.
- Tracking ad copy and landing pages reveals paid campaign strategies.
- Analyzing backlinks exposes link-building tactics.
Industry Reports and Publications
Market research reports and trade publications provide context on industry trends and competitor positioning.
- Reports from firms like Gartner or Statista highlight industry rankings and projections.
- Trade publications reveal emerging developments and competitive shifts.
Customer Feedback and Reviews
Competitor reviews offer direct insight into customer satisfaction, common issues, and unmet needs.
- Platforms like Trustpilot, G2, and Google Reviews showcase product strengths and weaknesses.
- Forum discussions highlight recurring problems in competitor products.
Conferences and Events
Industry events provide firsthand access to competitor strategies and upcoming initiatives.
- Product demos reveal how competitors position their offerings.
- Keynote speeches and panel discussions offer insights into future plans.
Job Postings and Hiring Trends
Hiring patterns signal investments in new technologies, products, or market expansions.
- Recruitment for AI engineers suggests innovation in automation or machine learning.
- Increased hiring in specific regions indicates geographic expansion.
Patent Databases and Intellectual Property
Patent filings expose competitors’ R&D focus and upcoming innovations.
- Recent patents signal new technologies in development.
- Patterns in filings reveal where competitors are investing their resources.
News and Media Coverage
News articles and press releases highlight major company moves, partnerships, and leadership direction.
- Coverage of mergers and acquisitions uncovers strategic realignments.
- Executive interviews shed light on company priorities and long-term goals.
Competitive intelligence isn’t just about collecting data, it’s about knowing where to look and turning insights into action.
Tools and Technologies in Competitive Intelligence

- Competitors App
- Features: Tracks competitors’ SEO, social media, ads, and content updates. Provides real-time alerts and automated, customizable reports.
- Advantages: Comprehensive monitoring, automated insights, customizable dashboards, and seamless integration with other tools.
- Disadvantages: May require initial setup time for tailoring reports to specific business needs.
- It’s Best For: Businesses seeking a streamlined, all-in-one solution for tracking and analyzing competitor activities.
- Pricing: $19 per month
- SEMrush
- Features: SEO analysis, keyword tracking, PPC insights, and competitor traffic monitoring.
- Advantages: User-friendly interface, detailed competitor benchmarking, and robust SEO tools.
- Disadvantages: Limited focus on areas outside of SEO and PPC.
- It’s Best For: Marketing teams looking to improve their SEO and PPC campaigns.
- Pricing: Starts at $129.95 per month.
- Ahrefs
- Features: Backlink analysis, keyword tracking, content gap identification, and rank tracking.
- Advantages: Excellent for backlink research and identifying keyword opportunities.
- Disadvantages: Requires a learning curve for beginners and lacks competitor social media monitoring.
- It’s Best For: SEO professionals focused on improving content and link-building strategies.
- Pricing: Starts at $129 per month.
- Crayon
- Features: Automated competitor tracking, customizable dashboards, and real-time alerts for website updates and campaigns.
- Advantages: Provides instant updates and covers multiple competitive intelligence areas effectively.
- Disadvantages: Higher pricing may not be suitable for small or mid-sized businesses.
- It’s Best For: Large enterprises looking for a robust and scalable competitive intelligence solution.
- Pricing: Custom pricing based on business size and requirements.
- BuzzSumo
- Features: Tracks trending content, analyzes social media engagement, and identifies influencers.
- Advantages: Great for content strategy and influencer marketing.
- Disadvantages: Limited utility outside of content and social media analysis.
- It’s Best For: Content marketers and social media managers aiming to improve engagement and outreach strategies.
- Pricing: Starts at $99 per month.
Emerging Technologies in Competitive Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI enhances competitive intelligence by processing vast amounts of data to detect trends and predict competitor actions.
- Example: AI-powered tools like Competitors App analyze historical data to spot shifts in competitor strategies.
Automation and Real-Time Insights
Automated systems collect and analyze data without manual effort, delivering real-time alerts for immediate decision-making.
- Example: Competitors App sends instant notifications about competitor activities, allowing businesses to respond quickly.
Advanced Data Visualization
Data visualization tools convert complex information into actionable insights through interactive dashboards.
- Example: Platforms like Tableau and Power BI present competitor data in clear, easy-to-digest visuals.
Ethical Considerations in Competitive Intelligence
Businesses must ensure ethical compliance when gathering and using competitor data.
- Use only publicly available and legally obtained data.
- Avoid unethical practices like misrepresentation, hacking, or accessing confidential information.
- Ensure compliance with data privacy laws such as GDPR.
Example: Platforms like Competitors App focus on ethical data collection, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Competitive Intelligence for SEO
Competitive intelligence helps businesses refine SEO strategies, identify gaps, and boost organic visibility.
Key Applications
- Competitor Keyword Analysis: Track high-performing keywords competitors rank for and optimize content accordingly.
- Content Gap Identification: Find topics competitors cover that your content lacks and create optimized versions.
- Backlink Opportunities: Analyze competitor backlink profiles to identify potential link-building prospects.
- Performance Monitoring: Observe how competitor SEO changes (like content updates) impact rankings and adjust your approach.
PPC Competitive Intelligence
Competitive intelligence reveals competitor ad strategies, helping businesses optimize ad spend and improve campaign results.
Key Applications
- Ad Strategy Analysis: Study competitors’ ad copy, visuals, and CTAs to refine messaging.
- Keyword Targeting: Identify the keywords competitors bid on and assess their effectiveness.
- Budget Allocation Insights: Estimate competitors’ ad spend and adjust budgets toward high-value opportunities.
- Campaign Optimization: Track which platforms (Google Ads, Facebook, LinkedIn) competitors prioritize and fine-tune ad placements.
How It Drives Results
- Improves SEO rankings through better keyword targeting and content optimization.
- Maximizes PPC efficiency by adjusting strategies based on competitor data.
Enhances competitive positioning by learning from competitor wins and failures.
Risks and Challenges of Competitive Intelligence
Ethical and Legal Risks
Failing to follow ethical and legal standards can damage reputation or result in legal consequences.
- Ethical Guidelines: Always use publicly available data; avoid misrepresentation or unauthorized data collection.
- Legal Compliance: Adhere to data privacy laws like GDPR to ensure responsible data usage.
- Best Practices: Platforms like Competitors App and Crayon ensure compliance by using ethical data sources.
Common Challenges
- Data Overload: Filtering out noise to focus on actionable insights can be difficult.
- Misinterpretation of Data: Poor analysis can lead to flawed strategic decisions.
- Overreliance on Competitors: Focusing too much on competitors can stifle innovation.
- Resource Allocation: Competitive intelligence requires time, tools, and skilled personnel.
Mitigating Risks and Challenges
- Use structured intelligence platforms to ensure reliable and well-organized data.
- Train teams on ethical data collection and proper analysis techniques.
- Balance competitor insights with innovation to maintain a proactive business strategy.
Competitive intelligence is a game-changer when done right, but only if businesses stay ethical, focused, and strategic.
How to get started with CI?
Building a Competitive Intelligence Culture
- Aligning CI with Business Objectives: Competitive intelligence should directly support your company’s goals. For example, if a company plans to enter a new market, CI can identify potential competitors, their pricing strategies, and gaps in their offerings. This alignment ensures that every insight gathered is actionable and contributes to strategic success.
- Fostering Collaboration: Competitive intelligence works best when multiple teams collaborate. Marketing teams can use CI to optimize campaigns, product teams can use it to innovate, and sales teams can refine pitches with competitor insights. For instance, a sales team armed with detailed data on a competitor’s pricing can confidently present value-based arguments during negotiations.
- Encouraging Proactive Thinking: Proactive CI identifies opportunities before competitors capitalize on them. For example, if a CI analysis reveals that competitors are investing heavily in a specific technology, it might indicate a future trend your business can explore ahead of time.
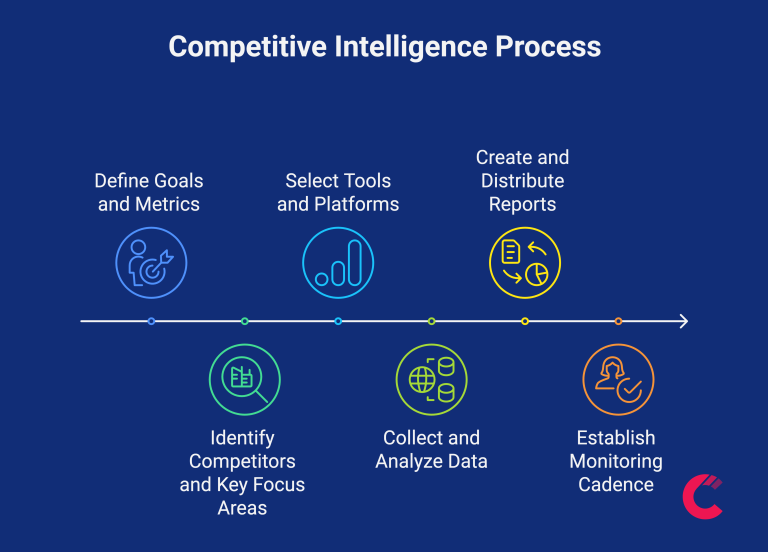
Setting Up a Competitive Intelligence Process
Step 1: Define Goals and Metrics
- Identify specific outcomes for your CI efforts. For instance:
- Increasing website traffic by 20% by targeting keywords competitors rank for.
- Launching a new product based on gaps identified in competitors’ offerings.
- Improving lead conversion rates by understanding competitor pricing structures.
Step 2: Identify Competitors and Key Focus Areas
- List direct competitors (e.g., those with similar products), indirect competitors (e.g., those targeting the same audience with different solutions), and emerging competitors (e.g., startups disrupting the market).
- Define what to monitor: marketing strategies, product features, pricing, or customer reviews. For example, a tech company might focus on tracking the product updates of rival software solutions.
Step 3: Select Tools and Platforms
- Use specialized platforms to gather intelligence efficiently:
- Competitors App: Best for tracking digital activities like SEO, social media, and content changes.
- SEMrush: Ideal for analyzing SEO and PPC strategies.
- BuzzSumo: Great for identifying top-performing competitor content.
Step 4: Collect and Analyze Data
- Gather data from publicly available sources like:
- Social media campaigns to gauge audience engagement.
- Competitor reviews on platforms like Trustpilot to understand customer sentiment.
- Annual reports to identify revenue drivers and investment priorities.
- Example: A clothing retailer might notice in reviews that customers complain about a competitor’s delivery speed, allowing them to focus on faster fulfillment as a competitive advantage.
Step 5: Create and Distribute Reports
- Tailor reports to the needs of different teams:
- For marketing: A detailed report on competitors’ SEO keywords and ad spend.
- For product teams: Insights on new features or customer feedback from competitor reviews.
- For executives: A summary of market opportunities and competitor threats.
- Example: A tech startup can use Competitors App to generate an automated weekly dashboard summarizing key competitor updates for leadership review.
Step 6: Establish Monitoring Cadence
- Set regular monitoring intervals based on industry dynamics:
- Daily tracking for fast-paced industries like e-commerce or technology.
- Monthly or quarterly reviews for slower-moving sectors like manufacturing.
- Example: A food delivery service might monitor competitors’ promotional campaigns weekly to stay competitive during peak periods.
Examples and Case Studies
Marketing
Competitive intelligence allows marketers to refine their campaigns by analyzing competitors’ strategies and identifying gaps.
- Example: Coca-Cola uses competitive intelligence to monitor rival campaigns, such as Pepsi’s Super Bowl ads, and adjust its own messaging for better impact.
- Case Study: In 2019, Pepsi launched a social media campaign targeting eco-conscious consumers. Coca-Cola responded by promoting its sustainability efforts, showcasing its investment in recyclable packaging.
- Application: By using tools like Competitors App, marketers can track the performance of competitors’ ad campaigns and pivot their strategies accordingly.
Product and Service Development
Understanding competitors’ product features, customer feedback, and pricing enables businesses to improve their offerings.
- Example: Samsung regularly monitors Apple’s product launches to identify gaps and differentiate its smartphones. This intelligence has driven innovations such as foldable screens and larger batteries.
- Case Study: Tesla disrupted the automotive industry by identifying that traditional car manufacturers overlooked electric vehicle demand. By analyzing gaps in customer satisfaction, Tesla designed EVs with high range and autonomous driving features.
- Application: Competitors App can help product teams track competitor updates, ensuring they stay ahead of trends and customer needs.
Sales
Sales teams benefit from CI by gaining insights into competitor pricing, promotions, and positioning.
- Example: A SaaS company might monitor competitors’ promotional discounts to tailor its own offerings. If a competitor offers a 20% discount, the sales team could emphasize the superior features of their product rather than competing solely on price.
- Case Study: Salesforce improved its pitch strategy by analyzing Oracle’s enterprise pricing model. It focused on emphasizing flexibility and integration as key selling points, winning over customers who found Oracle’s solutions rigid.
- Application: Real-time updates from competitive intelligence platforms allow sales teams to quickly adjust pitches and remain competitive.
Finance and Risk Management
CI helps finance teams analyze market conditions, competitor performance, and industry risks.
- Example: Netflix identified that competitors like Blockbuster were failing to invest in streaming technology. By investing heavily in this area early, Netflix minimized risk and became an industry leader.
- Case Study: When Disney+ launched, Netflix used competitive intelligence to analyze its pricing strategy and catalog, responding by ramping up original content to retain subscribers.
- Application: Risk managers can use CI tools to track competitor financial health, mergers, or acquisitions to anticipate market shifts.
Industry-Specific Examples
Healthcare
- Example: Pfizer closely monitors competitors’ drug development pipelines to stay ahead in launching new treatments.
- Case Study: During the COVID-19 pandemic, Pfizer analyzed Moderna’s rapid mRNA vaccine progress. Competitive intelligence helped Pfizer streamline its own vaccine development to compete effectively.
- Application: Tools like Competitors App can track clinical trial announcements and regulatory approvals for actionable insights.
Manufacturing
- Example: A car manufacturer might analyze how competitors optimize their supply chains to cut costs or improve efficiency.
- Case Study: Toyota used competitive intelligence to refine its lean manufacturing approach, outperforming competitors by reducing waste and improving production speed.
- Application: Monitoring supply chain innovations through CI can help manufacturers improve operations and reduce costs.
Technology
- Example: Google continuously monitors Apple and Amazon’s R&D investments to anticipate innovations in AI and voice assistants.
- Case Study: Microsoft analyzed Slack’s growth trajectory and competitive weaknesses to launch Microsoft Teams as a direct rival, offering seamless Office 365 integration as a competitive advantage.
- Application: CI platforms track patents, R&D investments, and market moves to guide strategic planning in tech companies.
Deliverables and Reporting in Competitive Intelligence
Key Deliverables
- Alerts and Watchlists
- Purpose: Real-time notifications about significant competitor activities, such as product launches, pricing changes, or new campaigns.
- Examples:
- Competitors App can send automated alerts when a competitor updates their website or social media strategy.
- A SaaS company could use alerts to track new feature rollouts by competitors, enabling faster responses.
- Dashboards and Reports
- Purpose: Visual summaries of competitor insights tailored for specific teams (marketing, sales, product, or leadership).
- Examples:
- Dashboards showcasing SEO keyword rankings, PPC performance, and competitor ad spend trends.
- Weekly competitor summary reports, including market positioning and customer sentiment analysis.
- Newsletters and Competitor Profiles
- Purpose: Regular updates and in-depth competitor profiles that provide a holistic view of their strategies.
- Examples:
- A newsletter summarizing a competitor’s recent campaigns and customer reviews.
- A profile detailing a competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, and future opportunities.
Making CI Actionable
- Communicating Insights Effectively
- Tailor reports to meet the needs of different stakeholders:
- Marketing: Focus on campaign comparisons and audience engagement metrics.
- Sales: Highlight competitor pricing strategies and promotional offers.
- Executives: Summarize high-level trends and strategic opportunities.
- Turning Data Into Results
- Actionable insights should drive decisions. Examples include:
- A retail brand tracking competitor discounts and adjusting its promotional calendar to stay competitive.
- A healthcare firm identifying a gap in treatment solutions based on competitor offerings and accelerating its product launch.
- Using Tools for Reporting
- Competitive intelligence platforms like Competitors App simplify the creation of professional, data-driven reports. They offer features like automated updates, customizable dashboards, and integration with other business tools to streamline workflows.
1. What are the goals of competitive intelligence?
The primary goals of competitive intelligence are to understand the competitive landscape, anticipate competitor moves, identify market opportunities, and inform strategic decision-making. It aims to provide insights that help businesses stay ahead of the competition, adapt to market changes, and capitalise on emerging trends.
2. What are the benefits of competitive intelligence in advertising?
In advertising, competitive intelligence helps in understanding competitors' advertising strategies, identifying effective messaging and channels, uncovering gaps in the market, and enhancing the effectiveness of your own campaigns. It leads to more targeted and impactful advertising efforts.
3. Are there any free tools to conduct competitor intelligence research?
Yes, there are free tools available for competitor intelligence research, such as Google Alerts for monitoring web mentions, social media platforms for engagement analysis, Ubersuggest for basic SEO insights, and SimilarWeb for traffic analysis. While these free tools provide valuable data, they might have limitations compared to paid platforms.
4. What is a competitive intelligence framework?
A competitive intelligence framework is a structured approach used to guide the collection, analysis, and application of competitive intelligence. It often involves steps like defining intelligence needs, gathering data, analysing information, and integrating insights into business strategies.
5. What are the most common competitive intelligence techniques and methods?
Common competitive intelligence techniques include SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), PESTLE analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental), competitor benchmarking, market segmentation analysis, and trend analysis.
6. How often should I conduct a competitor intelligence analysis?
Competitor intelligence analysis should be an ongoing process, but the frequency can vary depending on your industry’s dynamism and your specific business needs. It can range from weekly to quarterly. Key is to stay agile and responsive to any significant changes.
7. What are competitive intelligence systems?
Competitive intelligence systems are software and tools designed to systematically collect, store, analyse, and distribute competitive intelligence. These systems streamline the process of intelligence gathering and analysis, and often include features like real-time alerts, data visualisation, and reporting tools.
8. What is the most important source of competitive intelligence?
The most important source varies based on industry and business objectives. However, a combination of publicly available information, social media monitoring, market research reports, and direct competitor observations usually provides a comprehensive view.
9. Which marketing activity helps businesses gather information to compete effectively?
Content and social media analysis are key marketing activities for gathering competitive intelligence. They provide insights into competitors' engagement strategies, audience preferences, and content effectiveness.
10. Why is competitive intelligence important for SEO?
Competitive intelligence is crucial for SEO as it helps in understanding competitors' keyword strategies, backlink profiles, content tactics, and technical SEO aspects. This information is vital for optimising your own SEO strategies and improving search engine rankings.
11. What are the most successful competitive intelligence strategies?
The most successful strategies involve a continuous process of monitoring, analysing, and adapting. This includes regular competitor analysis, market trend observation, strategic use of tools like Competitors App, and integrating insights into decision-making.
12. What useful data can marketers gather from competitors?
Marketers can gather data on competitors' marketing campaigns, audience engagement, messaging and positioning, product launches, pricing strategies, and customer feedback. This data is invaluable for refining marketing tactics and identifying market opportunities.
13. Can I leverage competitive intelligence for B2B?
Absolutely. In B2B, competitive intelligence can be used to understand competitors’ product offerings, pricing models, sales strategies, and client relationships. It’s essential for identifying your competitive advantage and tailoring your offerings to meet the specific needs of your business clients.
14. How should competitor intelligence be gathered effectively?
Competitor intelligence should be gathered through a combination of ethical and systematic methods. Start by identifying key competitors and monitoring their public activities, such as website updates, social media posts, press releases, and product launches. Leverage tools like web scraping, analytics platforms, and specialized competitor tracking software to collect data efficiently. It's also essential to analyze industry reports, customer reviews, and market trends for additional insights. Always ensure your methods comply with legal and ethical guidelines to maintain integrity while gathering intelligence.
15. What is competitive marketing intelligence, and how is it gathered?
Competitive marketing intelligence is the process of collecting and analyzing publicly available data about competitors’ marketing strategies, customer behavior, and market trends. This intelligence is typically gathered through ethical means, such as monitoring competitors’ websites, social media campaigns, and advertisements. Tools like SEO trackers, social media analytics, and competitor monitoring platforms can help streamline the process. Additionally, studying industry reports, customer feedback, and market research provides valuable insights. The goal is to use this information to refine your own marketing strategies and gain a competitive edge in the market.
16. How Do You Compare Competitors Effectively?
Effective competitor analysis involves a systematic approach:
- Identify Key Competitors: Focus on direct, indirect, and emerging competitors.
- Gather Data: Use tools like Competitors App to track SEO, pricing, social media, and product updates.
- Analyze and Benchmark: Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning relative to your own.
- Act on Insights: Adjust your strategies based on the analysis, whether it’s improving products, refining marketing campaigns, or enhancing customer experiences.
17. Is Competitive Intelligence Ethical?
Yes, when conducted ethically. Competitive intelligence relies on publicly available data, such as websites, social media, and press releases. Avoid unethical practices like hacking, misrepresentation, or obtaining proprietary information without consent. Tools like Competitors App ensure compliance with ethical and legal standards.
18. How Do Businesses Use Competitive Intelligence for SEO and PPC?
Businesses use competitive intelligence to refine digital marketing strategies:
- SEO: Identify high-performing keywords, analyze content gaps, and study backlink profiles to improve rankings.
PPC: Track competitors’ ad copy, budgets, and keywords to optimize campaigns and maximize ROI.
For example, Competitors App provides real-time updates on competitors’ digital activities, ensuring businesses stay ahead in search and advertising strategies.


